- バックアップ一覧
- 差分 を表示
- 現在との差分 を表示
- ソース を表示
- STATE_tutorial/H2 へ行く。
Hydrogen molecule †
This tutorial explains how to perform the convergence study on the plane-wave cutoff and unit cell size and how to perform the geometry optimization of molecular system. With the periodic boundary condition, an isolated molecule is simulated by putting a molecule in a box that is large enough to avoid the interaction between periodic images. Here, we use a hydrogen atom with the local density approximation. The pseudopotential used is pot.H_lda1.
SCF calculation †
- Input file (nfinp_1)
0 0 0 0 0 0 : H2 molecule in a box 5.0 10.0 1 2 2 : GMAX GMAXP NTYP NATM NATM2 1 0 : NUM_SPACE_GROUP TYPE_OF_BRAVIS_LATTICE 10.0 10.0 10.0 90.0 90.0 90.0 : A B C ALPHA BETA GAMMA 1 1 1 1 1 1 : N1 N2 N3 M1 M2 M3 (k-point mesh and shift) 1 0 : NCORD NINV -0.710 0.000 0.000 1 1 1 : CPS(1:3) IWEI IMDTYP ITYP 0.710 0.000 0.000 1 1 1 : CPS(1:3) IWEI IMDTYP ITYP 1 0.15 1.00794 3 1 0.d0 : IATOMN ALFA AMION ILOC IVAN 0 0 0 0 0 : ICOND INIPOS INIVEL ININOS INIACC 0 1 : IPRE IPRI 200 200 0 57200.00 0 : NMD1 NMD2 ITER_LAST CPUMAX IFSTOP 3 1 : MIX_WAY MIX_WHAT 0 8 0.7 : STARTING_MIXING KBXMIX ALPHA 0.60 0.50 0.60 0.70 1.00 : DTIM1 DTIM2 DTIM3 DTIM4 DTIM_LAST 100.0 4 1 0.10D-08 : DTIO IMDALG IEXPL EDELTA 0.0010 0.50D+03 0 : WIDTH FORCCR ISTRESS ldapw91 1 : XCTYPE NSPIN 1.00 : DESTM 101 : NBZTYP 0 0 0 : DUMMY 0 0 0 : DUMMY 2 : NEG 1 : NEXTST 0 : DUMMY 2 : IMSD 0 : EVALUATE_EKO_DIFF 0 : NPDOSAO 0 0.0 : SM_N dopping - Execution
mpirun -np 4 ./STATE < nfinp_1 > nfout_1
- Results
When STATE is executed, the following greeting is printed*********************************************************************** * * * * * * * ****** ******** ** ******** ******** * * ******** ******** **** ******** ******** * * ** ** ** ** ** ** * * *** ** ******** ** ****** * * *** ** ********** ** ****** * * ** ** ** ** ** ** * * ******** ** ** ** ** ******** * * ****** ** VERSION 5.6.5 ** ******** * * RICS-AIST * * OSAKA UNIVERSITY * * * ***********************************************************************
At the convergence, following total energy and its component are printedTOTAL ENERGY AND ITS COMPONENTS TOTAL ENERGY = -1.13758782 A.U. FREE ENERGY = -1.13758782 A.U. KINETIC ENERGY = 0.96824571 A.U. HARTREE ENERGY = 0.73570075 A.U. XC ENERGY = -0.64555732 A.U. LOCAL ENERGY = -2.31372346 A.U. NONLOCAL ENERGY = -0.02336940 A.U. EWALD ENERGY = 0.14111590 A.U. PC ENERGY = 0.00000000 A.U. ENTROPIC ENERGY = 0.00000000 A.U.This is followed by the Fermi energy, the Kohn-Sham eigenvalues and the occupationFERMI ENERGY = -0.19018506 NKP= 1 NGP= 2103 K=( 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000) WKP= 1.0000 EIGEN VALUE -0.37074 -0.00963 OCCUPATION 1.00000 0.00000Further, the forces acting on atoms are printed outATOM COORDINATES FORCES MD: 1 MD: 1 H -0.710000 0.000000 0.000000 -0.01200 -0.00000 0.00000 MD: 2 H 0.710000 0.000000 0.000000 0.01200 -0.00000 0.00000
Convergence study †
In a calculation with a plane-wave basis set, kinetic energy cutoff for the plane-wave basis to expand the wave functions is one of the most important parameters to control the accuracy of the calculation. In the case of the ultrasoft pseudopotentials, cutoff energy for the augmentation charge should be specified, which is larger than 4 times larger than that for the wave functions. In the STATE code, cutoff wave vectors in the atomic unit for the wave functions (GMAX) and the augmentation charge (GMAXP) should be specified. GMAX**2 and GMAXP**2 are the cutoff energies in Ry.
By performing the total energy calculation with varying GMAX and GMAXP, we obtain the following [GMAXP=15 (E_cut^den=225 Ry)]
#GMAX ETOT (Ha) 4.0 -1.12781490 4.5 -1.13418820 5.0 -1.13697688 5.5 -1.13816998 6.0 -1.13847300 6.5 -1.13850127 7.0 -1.13851867 7.5 -1.13857102
[GMAXP=20 (E_cut^den=400 Ry)]
#GMAX ETOT (Ha) 4.0 -1.12780183 4.5 -1.13417130 5.0 -1.13695809 5.5 -1.13815036 6.0 -1.13845313 6.5 -1.13848136 7.0 -1.13849876 7.5 -1.13855109
[GMAXP=25 (E_cut^den=625 Ry)]
#GMAX ETOT (Ha) 4.0 -1.12780130 4.5 -1.13417074 5.0 -1.13695751 5.5 -1.13814979 6.0 -1.13845255 6.5 -1.13848078 7.0 -1.13849818 7.5 -1.13855052
[GMAXP=30 (E_cut^den=900 Ry)]
#GMAX ETOT (Ha) 4.0 -1.12780182 4.5 -1.13417124 5.0 -1.13695801 5.5 -1.13815027 6.0 -1.13845303 6.5 -1.13848127 7.0 -1.13849867 7.5 -1.13855100
With GMAX=6 and GMAXP=20, the total energy converges better than 0.1 mRy.
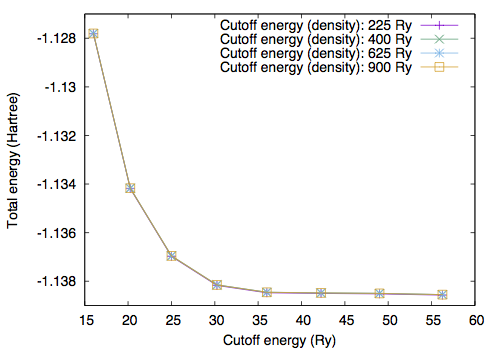
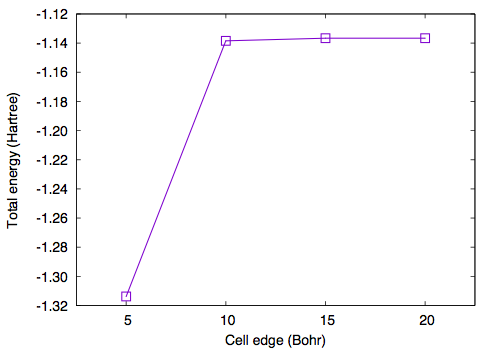
In addition to the cutoff energy, the convergence with respect to the unit cell size should be achieved to simulate an isolated molecule. Using GMAX=6 and GMAXP=20, total energy as a function of cell edge is obtained as follows
#A(Bohr) ETOT(Ha) 5.00 -1.31378028 10.00 -1.13845313 15.00 -1.13662806 20.00 -1.13661187
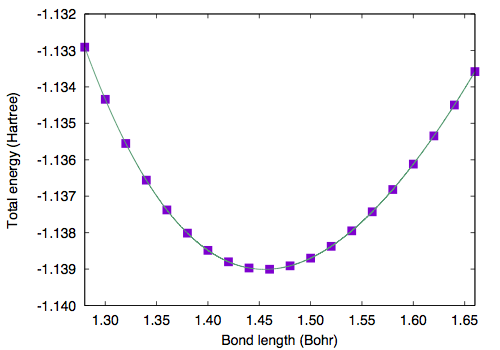
Geometry optimization (1) †
Geometry of a diatomic molecule can be optimized by calculating the total energy with varying bond length. Here the total energy as a function of bond length is shown. GMAX=6, GMAXP=20, and the unit cell edges of 10.0 Bohr is used.
1.28000000 -1.13291015 1.30000000 -1.13434083 1.32000000 -1.13555229 1.34000000 -1.13655937 1.36000000 -1.13737569 1.38000000 -1.13801370 1.40000000 -1.13848494 1.42000000 -1.13880026 1.44000000 -1.13896985 1.46000000 -1.13900337 1.48000000 -1.13890994 1.50000000 -1.13869810 1.52000000 -1.13837576 1.54000000 -1.13795024 1.56000000 -1.13742831 1.58000000 -1.13681622 1.60000000 -1.13611994 1.62000000 -1.13534513 1.64000000 -1.13449712 1.66000000 -1.13358088
By fitting the total energy to sixth order polynomial, equilibrium bond length of 1.4551 Bohr (0.77 Angstrom).
Geometry optimization (2) †
In a complex system, manual optimization is difficult to perform. In such a case, Hellmann-Feynman forces are used to perform the geometry optimization. To do so, we set the force criterion (FORCCR) of 1.e-3 to 1.e-4 Hartree/Bohr. Note that for SCF calculation, we set a large FORCCR such as 1.e+3 and avoid the structural optimization. In this example, generalized direct inversion of iterative subspace (GDIIS) method is used (IMDALG=4) with the time step of 100 atomic unit.
0 0 0 0 0 0 : H2 molecule in a box
6.0 20.0 1 2 2 : GMAX GMAXP NTYP NATM NATM2
1 0 : NUM_SPACE_GROUP TYPE_OF_BRAVIS_LATTICE
10.0 10.0 10.0 90.0 90.0 90.0 : A B C ALPHA BETA GAMMA
1 1 1 1 1 1 : N1 N2 N3 M1 M2 M3 (k-point mesh and shift)
1 0 : NCORD NINV
-0.710 0.000 0.000 1 1 1 : CPS(1:3) IWEI IMDTYP ITYP
0.710 0.000 0.000 1 1 1 : CPS(1:3) IWEI IMDTYP ITYP
1 0.15 1.00794 3 1 0.d0 : IATOMN ALFA AMION ILOC IVAN
0 0 0 0 0 : ICOND INIPOS INIVEL ININOS INIACC
0 1 : IPRE IPRI
200 200 0 57200.00 0 : NMD1 NMD2 ITER_LAST CPUMAX IFSTOP
3 1 : MIX_WAY MIX_WHAT
0 8 0.7 : STARTING_MIXING KBXMIX ALPHA
0.60 0.50 0.60 0.70 1.00 : DTIM1 DTIM2 DTIM3 DTIM4 DTIM_LAST
100.0 4 1 0.10D-08 : DTIO IMDALG IEXPL EDELTA
0.0010 0.50D-03 0 : WIDTH FORCCR ISTRESS
ldapw91 1 : XCTYPE NSPIN
1.00 : DESTM
101 : NBZTYP
0 0 0 : DUMMY
0 0 0 : DUMMY
2 : NEG
1 : NEXTST
0 : DUMMY
2 : IMSD
0 : EVALUATE_EKO_DIFF
0 : NPDOSAO
0 0.0 : SM_N dopping
Calculated equilibrium bond length is 1.455 Bohr (0.77 Angstrom), agreeing well with the one obtained by the total energy fitting.
![[PukiWiki] [PukiWiki]](image/logo_state-senri3_80x80.png)